ISIS: TIMELINE FOR THE RELIGIOUS AND SECTARIAN BACKGROUND.
630- Battle of Hunayn, Mohammed defeats the Hawazin Bedouins near Mecca. One of his followers, Huruqus ibn Zuhair, criticizes Mohammed for offering booty in return for converting to Islam. Mohammed predicts that he will betray Islam.
The Rashidun Caliphate (632-661): Ali and Abu Bakr: the split between the Shia and the Sunni

The Prophet Muhammed surrounded by the four Rashidun Caliph's
-632- 3 months before Mohammed's death, on his last pilgrimmage to mecca, Shiites believe that he stopped his caravan by a pond and said, "Do I not have more to say to you than all the others?" Followers ay 'yes'. Then he says, "All those whom I command shall also be commanded by Ali."
-but Abu Bakr, Mohammed's companion had been asked by the prophet to lead the prayers before his death, making him virtual leader.
-but after Mohammed's death in 632- many refuse to recongize Ali.
-Though Ali had been a close deputy and a military commander, Abu Bakr (632-634) became the Caliph or successor.
-637- Arab Muslims take Mesopotamia from the Persian Sassinids.
-Ali accepted the first two Caliphs Bakr and Omar
-656- assassination of third caliph- Osman by Egyptian rebels along with the the son of Omar. Ali appointed to Caliphate by the ruling tribe, the Quraysh. He decided not to punish the rebels severely. He was opposed by Aisha, wife of Muhammed and daughter of Abu Bakr who wanted rebels punished.
656-661- Caliphate of Ali
The First Fitna or Civil War and the formation of the Karijites
-"Following the murder of Caliph Uthman ibn Affan (Osman), the caliphate of the Muslim Empire passed to Ali the cousin and son-in-law of the Prophet Muhammad (Ali ibn Abi Talib the Prophet Muhammad’s cousin and son-in-law - the first Imam of Shia Islam). Shortly after ascending to the caliphate, Ali commenced consolidating his hold over the empire." (About.com)
- Muawiyah, a kinsman of the slain Uthman (Osman), refused to acknowledge Ali as caliph due his inability to bring the murderers to justice. In an attempt to avoid bloodshed, Ali sent an envoy, Jarir, to Syria to seek a peaceful solution. Jarir reported that Muawiyah would submit when the murderers were caught." (About.com)
- Muawiyah leads his army in an assault on the forces of Ali.
The Battle of Siffin.
657 AD- The Battle of Siffin- at Raqqa, on the Euphrates, between Ali Ibn Abi Talib and Muawiya at Al Raqqa, Syria. The battle is fought to a draw.

Battle of Siffin
-further negotiations fail when a faction on the side of Ali Ibn Abi Talib objects to Ali that negotiations with Muawiya are wrong because only Allah can decide.
The Karijites
-in Jufa, Iraq, the secessionists, known as Karijites (separatists), reject any further discussion with Ali. They form again in Nahrawan, Iraq, where they elect Abdullah ibn Wahb al-Rasibi and Hurqus ibn Zuhair (who had critcized Mohammed at the batttle of Hunayn in 630).

-the Kharijites "held that the judgment of God could only be expressed through the free choice of the entire Muslim community. They insisted that anyone, even a black slave, could be elected caliph (that is, head of the Muslim community) if he possessed the necessary qualifications, chiefly religious piety and moral purity. A caliph may be deposed upon the commission of any major sin. The Khārijites thus set themselves against the legitimist claims (to the Caliphate) of the tribe of Quraysh (among the Sunnites) and of ʿAlī’s descendants (among the Shīʿites). As proponents of the democratic principle, the Khārijites drew to themselves many who were dissatisfied with the existing political and religious authorities." -Encyclopedia Britannica On line.
"The historians al-Tabari and Ibn Kathir chronicle alarmingly precise accounts of their intimidation, violence and terror....Tey detail how the Khawarij began terrorizing the countryside around Nahrawan, Iraq, subjecting those whom they caught to an imtihan or “inquisition”. If the answers failed to satisfy their zeal for purity, or agree with their understanding of things, then the punishment was death." -Muslimmatters.org, Aug 24, 2015.
-at Nahrawan, when one of Ali's governors, Abdullah ibn Khabbaab al-Aratt, tries to reason with members of the newly founded Karijites, they hack him and his pregnant wife to death.
661- Kufa- assassination of Ali ibn Abi Talib- first imam- rightful successor to Mohammed. Killed by Kharijite extremists in the mosque of Kufa. (Shia = partisans of Ali). Shiites see this act as a rejection of the true succession by the Muslim majority. Buried at Najaf. Ali has since passed his own infallibility on to a series of Imams.
Umayyad Caliphate- 661-750.
661- Muawiyah is crowned head of the Muslim Empire in Jerusalem. He establishes the Umayyad Caliphate.

"...according to the Famous Hanbali scholar Ibn Taymiyya, Kharijites were the first to use excommunication processes against the rest of the Muslim community. Committing sin is viewed by Kharijites as a justifiable reason to excommunicate any Muslim who is not in accordance with their framework of interpreting major Islamic texts. They then find it lawful for them to fight supposed Muslim sinners and kill them." -Morocco World News, December 3, 2014.
683- " In the period of civil war (fitnah) following the death of the caliph Yazīd I (683), the Khārijites were the source of serious disruptions within the Umayyad domain and in Arabia. Subdued through the intensive campaigning of al-Ḥajjāj, the Khārijites did not stir again until the collapse of the Umayyads, and then their two major rebellions, in Iraq and Arabia, ended in defeat." - Encyclopedia Britannica on line.
745- circa- Muslim Millenarism: The earliest messianic figure in Islam was probably Jesus, who was taken up to heaven by God—rather than crucified (Koran 3:55) as in Christianity—with the understanding that he would return at the end of the world; the more prevalent figure, however, was that of the Mahdi, the rightly guided one. This title began to appear attached to prominent political and religious figures by the middle of the seventh century, but the predictions concerning him received their present form during the period of the Abbasid revolution (740–749): the Mahdi will arise in the east, in the region of Khorasan (today eastern Iran and Afghanistan), raise an army, march through the Iranian plateau to Iraq and establish his messianic kingdom there after purifying the Muslim world of evil. This scenario mirrored the Abbasid rise to power closely and served to legitimize their revolution. By contrast, the figure of Jesus remained in Muslim apocalyptic beliefs primarily to fight and slay the Dajjal (the Antichrist), who will appear prior to the messianic kingdom and test the Muslims. Jesus will return from heaven at the advent of the messianic age, slay the Dajjal near Jerusalem, and then pray behind the Mahdi. Read more: Islamic Millenarianism - Bibliography - Messianic, Muslim, Apocalyptic, and World - JRank Articles http://science.jrank.org/pages/7870/Islamic-Millenarianism.html#ixzz3kvmUQaWp
Hanbal
780-855- Ahmad Ibn Hanbal, sounder of the Hanbali code of Sharia law. He holds that a decision in Sharia must be referred directly to the Quran and the sunna- not to the legal framework that had grown up around them. In other words, he held that the law itself had already been written in the words of the Quran.

-in subsequent centuries, the Hanbali Code loses strength everywhere except at Najd in central Arabia.
Taqi al-Deen Ahmad Ibn Taymiyya (1268-1328AD)
1300- Taqi al-Deen Ahmad Ibn Taymiyy: "The mediæval Hanbali professor Ibn Taymiyya has been the most important inspiration for Sunni radicals of the modern era, and indeed he is respected for his scholarship by many non-radical Sunnis, despite the considerable reservations they express about his radicalism.1 Ibn Taymiyya was more outspoken than Ahmad bin Hanbal2 and lived in a time in which Islam was exposed to unusual pressure, most notably the conquest of the Abbasid Caliphate by the heathen Mongols in 1258 AD.3 These two factors help explain the revival by radicals of Ibn Taymiyya's legacy in the face of secularism, colonialism and the decline of the international prestige of the Umma (Muslim community) during the modern age." http://www.pwhce.org/taymiyyah.html

Ibn Tayamiyya
The Wahhabi Movement of the 18th Century.
1703- Abdul al-Wahhab is born at Najd, a main centre of Hanbali Islam in the heart of the Arabian Peninsula.
1725 (circa) -Al-Wahhab (1703-1787) founds Muwahidun (unitarian) movement- an attempt to purify Islam of medieval superstition, to stop the translation of Sharia into jurisprudence and to get rid of the cult of saints. The Muwahidun follow the Hanbali school as taught by Tarq al Din ibn Taimiya (qv). Wahhab's oponnents call his followers 'Wahhabis', the name that stuck.
-Wahhab makes attendance at public prayer obligatory, forbids the building of minarets,
Ibn Saud, Wahhabism and the Origins of the House of Saud
-having failed to spread his movement, Al Wahhab allies himself with a tribal chieftain, Mohammed Ib Saud.
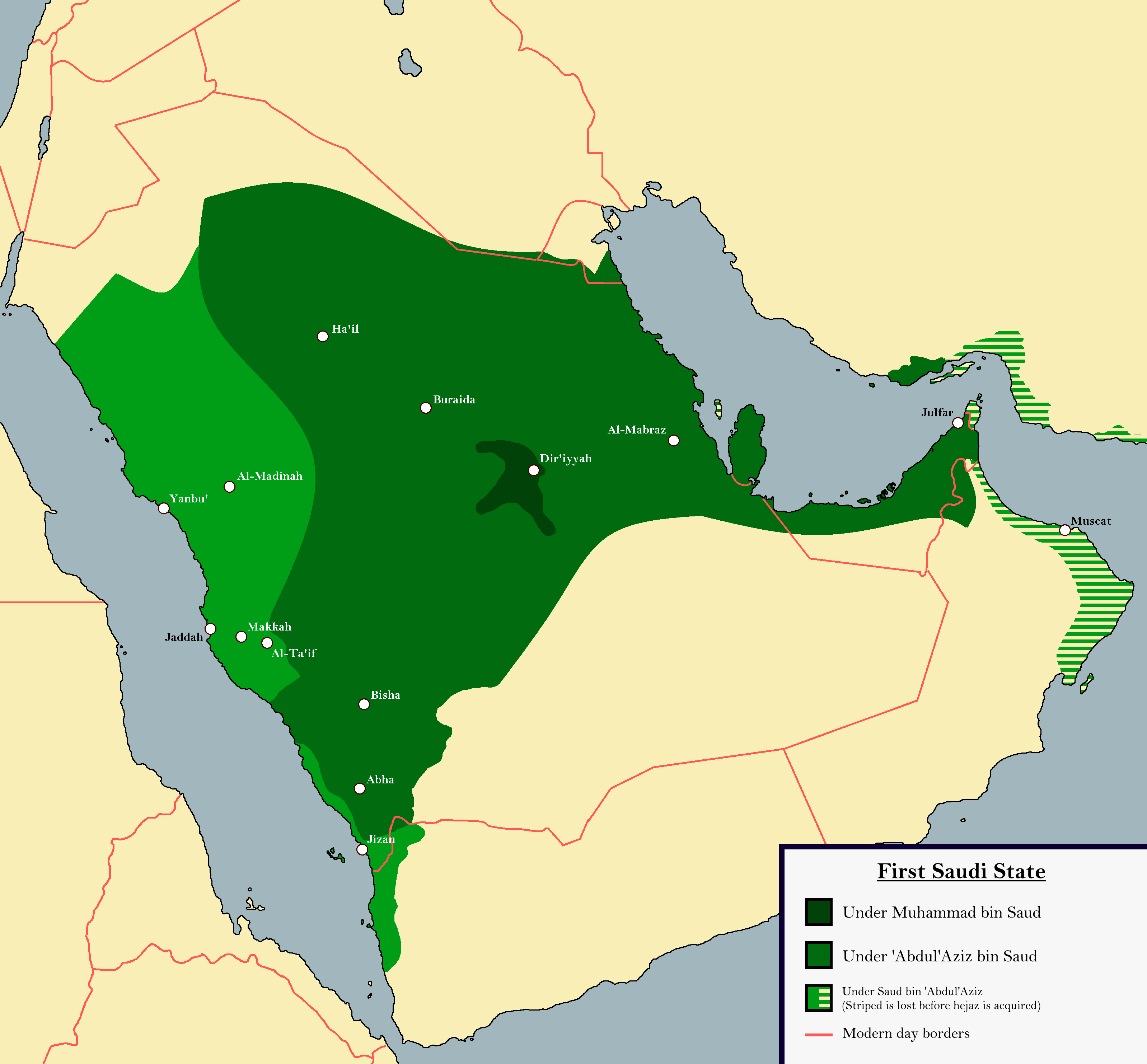
1726-65- Mohammed Ibn Saud, ruler of the Diraiya Emirate embraces Wahhabism, has his subjects convert on pain of death.
1745- Muhammad Ibn Saud becomes ruler of Najd, the central plateau and oasis region of Arania, founds the House of Saud.
-in alliance with followers of Saud, Wahabbis mount a campaign against idolatry, corruption and adultery. On the authority of the Hadith, they ban dancing, music and poetry, silk, gold, ornaments and jewelery.
1766-1803- Mohammed's son, Abdul Aziz Ibn Saud, continues to uphold Wahhabism.
1773- Abdul Aziz ibn Saud takes Riyadh.
1802- in a campaign against the Shia, the Wahhabis attack the Shia holy city of Karbala.
1810- the Whhabi Ibn Sauds ruule most of Arabia.
1803-1814 Saud Ibn Abdul Aziz of the House of Saud tries to spread Wahhabism to the frontiers of Syria and Iraq.
The Ottoman Sultan sends the Egyptian Pasha to Crush Wahhabism.
-the Ottoman Sultan is outrages by what he sees as descecration of the holy pplaces of Arabi by the Sauds and their Wahhabism.
1814-18- Sent by hte sultan, Muhammad Ali, Viceroy of Egypt, crushes the Wahhabist movement and executes Abdullah Ibn Saud.
Salafism
1838-97- Jamal al-din Afghani. Helps develop Salafism- an Islamic ideology based on the example of the salaf- the ancestors of early Islam. He promotes the Pan-Islam movement in an attempt to revive a mythical 'pure' Islam free of ethnic and political rivalries.
1849-1905- Muhammad Abdu- a follower of Afghani (b. 1838) emphasized the influence of the Salaf on Sharia law.
1865-1935- Muhammad Rashid Rida, follower of Abdu (b. 1849) researched what Mohammed and 'the pious ancestors' had done and taught so that it could be applied to contemporary conditions. He preferred the Salaf to the four Sunni legal schools.
Fall and Revival of Wahhabism
1881- House of Saud expelled from the Riyadh region. But it revivies under Abdul Rahman Ibn Al Saud and spreads Wahhabism
1891- Abdul Rahman Ibn Al Saud of the House of Saud is overthrown at Diraiya by the House Of Rashid which has Ottoman backing.
1902 -Abdul Aziz ibn Abdul Rahman al Saud re-conquers the Najd from the Ottomans, reviviing Wahhabism militarily and politically through the Ikhwan Wahhabist movement. Wahabbis mount new attacks on hypocrites, laxity, non-blievers. The criteria for belief is strict adherecne to the Sharia.
1905-6- Abdul Aziz Ibn Abdul Rahman takes east central Arabia.
1913- Abdul Aziz Ibn Saud, commander of the Whhabist Ikhwan army invades the Shia region of Al-Hasa and attempts to impose Wahhabism.
1920s- Salafis teach that since Mohammed was chosen by the community, leadership of Islam cannot be hereditary.
1925- Ibn Saud's Ikhwan Wahhabists destroy the Jannat al Baghi cemetery in Medina, a Shia holy place where the daughter of the Prophet and the 3nd, 4th, 5th and 6th Shia imams are buried.
1926- The Ikhwan resorts to the systematic killing of Shia.
1927- May 20- British lay down treaty of Jeddah giving the Hijaz and Jajd to Abdul Aziz Ibn Saud. The Ikhwan, sends a Wahhabi recolt against Ibn Saud for using telephone,s radios, cars etc.
The Saudi Domestication of Wahhabism.
1928- Muslim Brotherhood founded by Hassan al Banna in Egypt for moral and social reform.
1930s- House of Saud becomes rich on oil wealth, moderates its belief in Wahhabism; the pogroms against the Shia are stopped; instead the Shia suffer discrimination and marginalization.
1932- the vast desert region whose heart is the Najd bcomes the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
-in Mecca, the Supreme Religious Council continues to be the official head of Wahabbism.
Uprising against Saudis; beginning of Careers of Osama Bin Laden and Ayman Zawahiri.
1978- Ayman Zawahiri graduates as as a surgeon from Cairo's University's medical school.
-Bin Laden graduates with a degree in civil engineering from King Abdul Aziz University in Saudi Arabia.
1979- armed uprising against rulers of Saudi Arabia at the Grand Mosque- assisted by Salafis from Kuwait. The young engineering graduate, Bin laden, regards them as true Muslims. Salafis have since become active in Kuwait politics.
1979- Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Begin sign the Egyptian-Istaeli peace Treaty. But his new peace costs Egypt membership in the Arab League.
-due to the unpopularity of the treaty at home, Sadat becomes increasingly autocratic.
Roots of the Al Nusra Front.
1980- Abu Musab al Sur (aka Mustafa Setmariam Nasar and the intellectual godfather of Al Nusra) joins the Combatant Vanguard organization, a radical offshoot of the Syrian Muslim Brotherhood which is at the forefront in the Islamic uprising in Hama, Syria.
Abdullah Azzam's 'Bureau of Service' in Pakistan for Afghan Jihad- antecedent to Al Qaeda.
1980- Abdullah Azzam founds Maktab al Khidmat (Bureau of Service) in Peshawar, Pakistan.
-Pakistani ISI and American CIA camps along the Afghan-Pakistan border join in training non-Afhgan Mujehadeen to fight the Soviets in Afghanistan. They use US army training manuals translated into Urdu, Arabic and Persian, stressing nationalism and Islam.
-Bin Laden visits Peshawar and lobbies family and friends to support the anti-Soviet jihad in Afghanistan.
-Osama Bin Laden goes back to Saudi Arabia, raises large sums from family connections and returns to Pakistan with members of the family business, the Saudi Binlandin Group.
Bin Laden and Tyamiyya
Osama often cited Ibn Taymiyyah in his sermons and communiqués. On one occasion he said:
The most important religious duty – after belief itself – is to ward off and fight the enemy aggressor. Šayḫ al-Islam (Ibn Taymiyyah), may Allāh have mercy upon him, said: “to drive off the enemy aggressor who destroys both religion and the world – there is no religious duty more important than this, apart from belief itself. This is an unconditional rule.” -http://www.shiapac.org/2015/02/07/from-ibn-e-taymiyyah-to-daish-isisisil-by-sidq-miqal/
thanks to BBC Timelines and:
TheIndependent on Sunday
http://www.cnsnews.com/news/article/patrick-goodenough/timeline-al-qaeda-linked-terrorists-move-closer-establishing-islamic
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/10895006/Timeline-How-al-Qaeda-regained-its-hold-in-Iraq.html
-http://www.cbc.ca/news/world/story/2011/05/02/f-al-qaeda-timeline.html
- Infoplease.com http://www.infoplease.com/spot/al-qaeda-terrorism.html#ixzz2Rg9JhBiu
630- Battle of Hunayn, Mohammed defeats the Hawazin Bedouins near Mecca. One of his followers, Huruqus ibn Zuhair, criticizes Mohammed for offering booty in return for converting to Islam. Mohammed predicts that he will betray Islam.
The Rashidun Caliphate (632-661): Ali and Abu Bakr: the split between the Shia and the Sunni

The Prophet Muhammed surrounded by the four Rashidun Caliph's
-632- 3 months before Mohammed's death, on his last pilgrimmage to mecca, Shiites believe that he stopped his caravan by a pond and said, "Do I not have more to say to you than all the others?" Followers ay 'yes'. Then he says, "All those whom I command shall also be commanded by Ali."
-but Abu Bakr, Mohammed's companion had been asked by the prophet to lead the prayers before his death, making him virtual leader.
-but after Mohammed's death in 632- many refuse to recongize Ali.
-Though Ali had been a close deputy and a military commander, Abu Bakr (632-634) became the Caliph or successor.
-637- Arab Muslims take Mesopotamia from the Persian Sassinids.
-Abu Bakr
succeeded by Omar (634-644) and the third Caliph Osman- (644-656) followers from
the old Arab aristocracy of Mecca- recent allies of Mohammed. Ali could
not accept Osman and joined opposition because, though he differed on
matters of doctrine with Bakr and Omar, his differences with Osman were
severe. Osman followed by Hazrat Ali.
-Ali accepted the first two Caliphs Bakr and Omar
-656- assassination of third caliph- Osman by Egyptian rebels along with the the son of Omar. Ali appointed to Caliphate by the ruling tribe, the Quraysh. He decided not to punish the rebels severely. He was opposed by Aisha, wife of Muhammed and daughter of Abu Bakr who wanted rebels punished.
656-661- Caliphate of Ali
The First Fitna or Civil War and the formation of the Karijites
-"Following the murder of Caliph Uthman ibn Affan (Osman), the caliphate of the Muslim Empire passed to Ali the cousin and son-in-law of the Prophet Muhammad (Ali ibn Abi Talib the Prophet Muhammad’s cousin and son-in-law - the first Imam of Shia Islam). Shortly after ascending to the caliphate, Ali commenced consolidating his hold over the empire." (About.com)
-the governor of Damascus, Mu’awiyah, was one of Ali’s principal opponents
- Muawiyah, a kinsman of the slain Uthman (Osman), refused to acknowledge Ali as caliph due his inability to bring the murderers to justice. In an attempt to avoid bloodshed, Ali sent an envoy, Jarir, to Syria to seek a peaceful solution. Jarir reported that Muawiyah would submit when the murderers were caught." (About.com)
- Muawiyah leads his army in an assault on the forces of Ali.
The Battle of Siffin.
657 AD- The Battle of Siffin- at Raqqa, on the Euphrates, between Ali Ibn Abi Talib and Muawiya at Al Raqqa, Syria. The battle is fought to a draw.

Battle of Siffin
-further negotiations fail when a faction on the side of Ali Ibn Abi Talib objects to Ali that negotiations with Muawiya are wrong because only Allah can decide.
The Karijites
-in Jufa, Iraq, the secessionists, known as Karijites (separatists), reject any further discussion with Ali. They form again in Nahrawan, Iraq, where they elect Abdullah ibn Wahb al-Rasibi and Hurqus ibn Zuhair (who had critcized Mohammed at the batttle of Hunayn in 630).
-the Kharijites "held that the judgment of God could only be expressed through the free choice of the entire Muslim community. They insisted that anyone, even a black slave, could be elected caliph (that is, head of the Muslim community) if he possessed the necessary qualifications, chiefly religious piety and moral purity. A caliph may be deposed upon the commission of any major sin. The Khārijites thus set themselves against the legitimist claims (to the Caliphate) of the tribe of Quraysh (among the Sunnites) and of ʿAlī’s descendants (among the Shīʿites). As proponents of the democratic principle, the Khārijites drew to themselves many who were dissatisfied with the existing political and religious authorities." -Encyclopedia Britannica On line.
"The historians al-Tabari and Ibn Kathir chronicle alarmingly precise accounts of their intimidation, violence and terror....Tey detail how the Khawarij began terrorizing the countryside around Nahrawan, Iraq, subjecting those whom they caught to an imtihan or “inquisition”. If the answers failed to satisfy their zeal for purity, or agree with their understanding of things, then the punishment was death." -Muslimmatters.org, Aug 24, 2015.
-at Nahrawan, when one of Ali's governors, Abdullah ibn Khabbaab al-Aratt, tries to reason with members of the newly founded Karijites, they hack him and his pregnant wife to death.
661- Kufa- assassination of Ali ibn Abi Talib- first imam- rightful successor to Mohammed. Killed by Kharijite extremists in the mosque of Kufa. (Shia = partisans of Ali). Shiites see this act as a rejection of the true succession by the Muslim majority. Buried at Najaf. Ali has since passed his own infallibility on to a series of Imams.
Umayyad Caliphate- 661-750.
661- Muawiyah is crowned head of the Muslim Empire in Jerusalem. He establishes the Umayyad Caliphate.
"...according to the Famous Hanbali scholar Ibn Taymiyya, Kharijites were the first to use excommunication processes against the rest of the Muslim community. Committing sin is viewed by Kharijites as a justifiable reason to excommunicate any Muslim who is not in accordance with their framework of interpreting major Islamic texts. They then find it lawful for them to fight supposed Muslim sinners and kill them." -Morocco World News, December 3, 2014.
683- " In the period of civil war (fitnah) following the death of the caliph Yazīd I (683), the Khārijites were the source of serious disruptions within the Umayyad domain and in Arabia. Subdued through the intensive campaigning of al-Ḥajjāj, the Khārijites did not stir again until the collapse of the Umayyads, and then their two major rebellions, in Iraq and Arabia, ended in defeat." - Encyclopedia Britannica on line.
745- circa- Muslim Millenarism: The earliest messianic figure in Islam was probably Jesus, who was taken up to heaven by God—rather than crucified (Koran 3:55) as in Christianity—with the understanding that he would return at the end of the world; the more prevalent figure, however, was that of the Mahdi, the rightly guided one. This title began to appear attached to prominent political and religious figures by the middle of the seventh century, but the predictions concerning him received their present form during the period of the Abbasid revolution (740–749): the Mahdi will arise in the east, in the region of Khorasan (today eastern Iran and Afghanistan), raise an army, march through the Iranian plateau to Iraq and establish his messianic kingdom there after purifying the Muslim world of evil. This scenario mirrored the Abbasid rise to power closely and served to legitimize their revolution. By contrast, the figure of Jesus remained in Muslim apocalyptic beliefs primarily to fight and slay the Dajjal (the Antichrist), who will appear prior to the messianic kingdom and test the Muslims. Jesus will return from heaven at the advent of the messianic age, slay the Dajjal near Jerusalem, and then pray behind the Mahdi. Read more: Islamic Millenarianism - Bibliography - Messianic, Muslim, Apocalyptic, and World - JRank Articles http://science.jrank.org/pages/7870/Islamic-Millenarianism.html#ixzz3kvmUQaWp
Hanbal
780-855- Ahmad Ibn Hanbal, sounder of the Hanbali code of Sharia law. He holds that a decision in Sharia must be referred directly to the Quran and the sunna- not to the legal framework that had grown up around them. In other words, he held that the law itself had already been written in the words of the Quran.
-in subsequent centuries, the Hanbali Code loses strength everywhere except at Najd in central Arabia.
Taqi al-Deen Ahmad Ibn Taymiyya (1268-1328AD)
1300- Taqi al-Deen Ahmad Ibn Taymiyy: "The mediæval Hanbali professor Ibn Taymiyya has been the most important inspiration for Sunni radicals of the modern era, and indeed he is respected for his scholarship by many non-radical Sunnis, despite the considerable reservations they express about his radicalism.1 Ibn Taymiyya was more outspoken than Ahmad bin Hanbal2 and lived in a time in which Islam was exposed to unusual pressure, most notably the conquest of the Abbasid Caliphate by the heathen Mongols in 1258 AD.3 These two factors help explain the revival by radicals of Ibn Taymiyya's legacy in the face of secularism, colonialism and the decline of the international prestige of the Umma (Muslim community) during the modern age." http://www.pwhce.org/taymiyyah.html

Ibn Tayamiyya
The Wahhabi Movement of the 18th Century.
1703- Abdul al-Wahhab is born at Najd, a main centre of Hanbali Islam in the heart of the Arabian Peninsula.
1725 (circa) -Al-Wahhab (1703-1787) founds Muwahidun (unitarian) movement- an attempt to purify Islam of medieval superstition, to stop the translation of Sharia into jurisprudence and to get rid of the cult of saints. The Muwahidun follow the Hanbali school as taught by Tarq al Din ibn Taimiya (qv). Wahhab's oponnents call his followers 'Wahhabis', the name that stuck.
-Wahhab makes attendance at public prayer obligatory, forbids the building of minarets,
Ibn Saud, Wahhabism and the Origins of the House of Saud
-having failed to spread his movement, Al Wahhab allies himself with a tribal chieftain, Mohammed Ib Saud.

1726-65- Mohammed Ibn Saud, ruler of the Diraiya Emirate embraces Wahhabism, has his subjects convert on pain of death.
1745- Muhammad Ibn Saud becomes ruler of Najd, the central plateau and oasis region of Arania, founds the House of Saud.
-in alliance with followers of Saud, Wahabbis mount a campaign against idolatry, corruption and adultery. On the authority of the Hadith, they ban dancing, music and poetry, silk, gold, ornaments and jewelery.
1766-1803- Mohammed's son, Abdul Aziz Ibn Saud, continues to uphold Wahhabism.
1773- Abdul Aziz ibn Saud takes Riyadh.
1802- in a campaign against the Shia, the Wahhabis attack the Shia holy city of Karbala.
1810- the Whhabi Ibn Sauds ruule most of Arabia.
1803-1814 Saud Ibn Abdul Aziz of the House of Saud tries to spread Wahhabism to the frontiers of Syria and Iraq.
The Ottoman Sultan sends the Egyptian Pasha to Crush Wahhabism.
-the Ottoman Sultan is outrages by what he sees as descecration of the holy pplaces of Arabi by the Sauds and their Wahhabism.
1814-18- Sent by hte sultan, Muhammad Ali, Viceroy of Egypt, crushes the Wahhabist movement and executes Abdullah Ibn Saud.
Salafism
1838-97- Jamal al-din Afghani. Helps develop Salafism- an Islamic ideology based on the example of the salaf- the ancestors of early Islam. He promotes the Pan-Islam movement in an attempt to revive a mythical 'pure' Islam free of ethnic and political rivalries.
1849-1905- Muhammad Abdu- a follower of Afghani (b. 1838) emphasized the influence of the Salaf on Sharia law.
1865-1935- Muhammad Rashid Rida, follower of Abdu (b. 1849) researched what Mohammed and 'the pious ancestors' had done and taught so that it could be applied to contemporary conditions. He preferred the Salaf to the four Sunni legal schools.
Fall and Revival of Wahhabism
1881- House of Saud expelled from the Riyadh region. But it revivies under Abdul Rahman Ibn Al Saud and spreads Wahhabism
1891- Abdul Rahman Ibn Al Saud of the House of Saud is overthrown at Diraiya by the House Of Rashid which has Ottoman backing.
1902 -Abdul Aziz ibn Abdul Rahman al Saud re-conquers the Najd from the Ottomans, reviviing Wahhabism militarily and politically through the Ikhwan Wahhabist movement. Wahabbis mount new attacks on hypocrites, laxity, non-blievers. The criteria for belief is strict adherecne to the Sharia.
1905-6- Abdul Aziz Ibn Abdul Rahman takes east central Arabia.
1913- Abdul Aziz Ibn Saud, commander of the Whhabist Ikhwan army invades the Shia region of Al-Hasa and attempts to impose Wahhabism.
1920s- Salafis teach that since Mohammed was chosen by the community, leadership of Islam cannot be hereditary.
1925- Ibn Saud's Ikhwan Wahhabists destroy the Jannat al Baghi cemetery in Medina, a Shia holy place where the daughter of the Prophet and the 3nd, 4th, 5th and 6th Shia imams are buried.
1926- The Ikhwan resorts to the systematic killing of Shia.
1927- May 20- British lay down treaty of Jeddah giving the Hijaz and Jajd to Abdul Aziz Ibn Saud. The Ikhwan, sends a Wahhabi recolt against Ibn Saud for using telephone,s radios, cars etc.
The Saudi Domestication of Wahhabism.
1928- Muslim Brotherhood founded by Hassan al Banna in Egypt for moral and social reform.
1930s- House of Saud becomes rich on oil wealth, moderates its belief in Wahhabism; the pogroms against the Shia are stopped; instead the Shia suffer discrimination and marginalization.
1932- the vast desert region whose heart is the Najd bcomes the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
-in Mecca, the Supreme Religious Council continues to be the official head of Wahabbism.
Uprising against Saudis; beginning of Careers of Osama Bin Laden and Ayman Zawahiri.
1978- Ayman Zawahiri graduates as as a surgeon from Cairo's University's medical school.
-Bin Laden graduates with a degree in civil engineering from King Abdul Aziz University in Saudi Arabia.
1979- armed uprising against rulers of Saudi Arabia at the Grand Mosque- assisted by Salafis from Kuwait. The young engineering graduate, Bin laden, regards them as true Muslims. Salafis have since become active in Kuwait politics.
1979- Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Begin sign the Egyptian-Istaeli peace Treaty. But his new peace costs Egypt membership in the Arab League.
-due to the unpopularity of the treaty at home, Sadat becomes increasingly autocratic.
Roots of the Al Nusra Front.
1980- Abu Musab al Sur (aka Mustafa Setmariam Nasar and the intellectual godfather of Al Nusra) joins the Combatant Vanguard organization, a radical offshoot of the Syrian Muslim Brotherhood which is at the forefront in the Islamic uprising in Hama, Syria.
Abdullah Azzam's 'Bureau of Service' in Pakistan for Afghan Jihad- antecedent to Al Qaeda.
1980- Abdullah Azzam founds Maktab al Khidmat (Bureau of Service) in Peshawar, Pakistan.
-Pakistani ISI and American CIA camps along the Afghan-Pakistan border join in training non-Afhgan Mujehadeen to fight the Soviets in Afghanistan. They use US army training manuals translated into Urdu, Arabic and Persian, stressing nationalism and Islam.
-Bin Laden visits Peshawar and lobbies family and friends to support the anti-Soviet jihad in Afghanistan.
-Osama Bin Laden goes back to Saudi Arabia, raises large sums from family connections and returns to Pakistan with members of the family business, the Saudi Binlandin Group.
Bin Laden and Tyamiyya
Osama often cited Ibn Taymiyyah in his sermons and communiqués. On one occasion he said:
The most important religious duty – after belief itself – is to ward off and fight the enemy aggressor. Šayḫ al-Islam (Ibn Taymiyyah), may Allāh have mercy upon him, said: “to drive off the enemy aggressor who destroys both religion and the world – there is no religious duty more important than this, apart from belief itself. This is an unconditional rule.” -http://www.shiapac.org/2015/02/07/from-ibn-e-taymiyyah-to-daish-isisisil-by-sidq-miqal/
thanks to BBC Timelines and:
TheIndependent on Sunday
http://www.cnsnews.com/news/article/patrick-goodenough/timeline-al-qaeda-linked-terrorists-move-closer-establishing-islamic
http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-middle-east-23283079
Wikipedia,
http://www.al-monitor.com/pulse/originals/2013/04/al-qaeda-jabhat-al-nusra-merge.html
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/10895006/Timeline-How-al-Qaeda-regained-its-hold-in-Iraq.html
-http://www.cbc.ca/news/world/story/2011/05/02/f-al-qaeda-timeline.html
- Infoplease.com http://www.infoplease.com/spot/al-qaeda-terrorism.html#ixzz2Rg9JhBiu
No comments :
Post a Comment